Appearance
一、前言回顾
前篇文章提到手动释放锁的lua脚本,当线程完全释放锁后,就会调用cancelExpirationRenewal()方法取消"看门狗"的续时线程 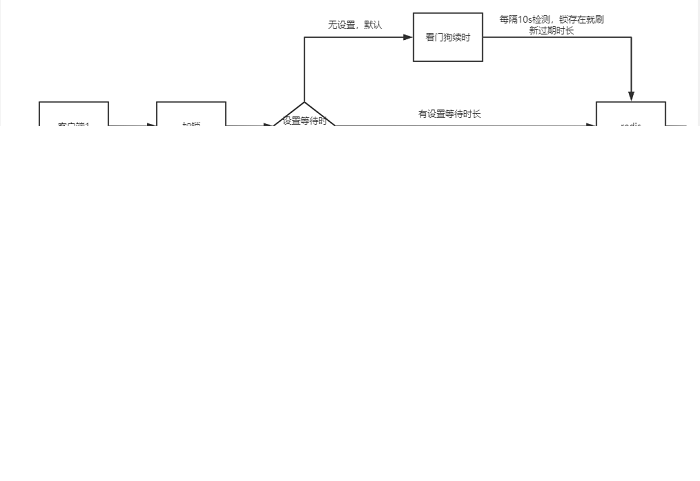
前篇文章入口:09_redis分布式锁(六):可重入锁源码剖析之释放锁
二、尝试获取锁超时
之前我们使用获取锁是lock方法,接下来我们介绍一下第二个方法tryLock,tryLock()方法是有返回值的,它表示用来尝试获取锁,如果获取成功,则返回true,如果获取失败(即锁已被其他线程获取),则返回false,这个方法无论如何都会立即返回。在拿不到锁时不会一直在那等待
java
public boolean tryLock(long waitTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
return this.tryLock(waitTime, -1L, unit);
}
public boolean tryLock(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
long time = unit.toMillis(waitTime);
long current = System.currentTimeMillis();
final long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
Long ttl = this.tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
if (ttl == null) {
return true;
} else {
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current;
if (time <= 0L) {
this.acquireFailed(threadId);
return false;
} else {
current = System.currentTimeMillis();
final RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> subscribeFuture = this.subscribe(threadId);
if (!this.await(subscribeFuture, time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {
if (!subscribeFuture.cancel(false)) {
subscribeFuture.addListener(new FutureListener<RedissonLockEntry>() {
public void operationComplete(Future<RedissonLockEntry> future) throws Exception {
if (subscribeFuture.isSuccess()) {
RedissonLock.this.unsubscribe(subscribeFuture, threadId);
}
}
});
}
this.acquireFailed(threadId);
return false;
} else {
boolean var14;
try {
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current;
if (time > 0L) {
boolean var16;
do {
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
ttl = this.tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
if (ttl == null) {
var16 = true;
return var16;
}
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;
if (time <= 0L) {
this.acquireFailed(threadId);
var16 = false;
return var16;
}
currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (ttl >= 0L && ttl < time) {
this.getEntry(threadId).getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
this.getEntry(threadId).getLatch().tryAcquire(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;
} while(time > 0L);
this.acquireFailed(threadId);
var16 = false;
return var16;
}
this.acquireFailed(threadId);
var14 = false;
} finally {
this.unsubscribe(subscribeFuture, threadId);
}
return var14;
}
}
}
}看到这个源码就发现和lock 是很像的,Long ttl = this.tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId); 又回到了之前lock的逻辑,先来分析一下里面的几个参数time�、current�、threadId�
java
//time = waitTime,是我们指定的最大的等待获取锁的时间
//current = 第一次尝试获取锁之前的一个时间戳
//threadId = 当前操作的线程ID当我们的if (ttl == null) 的时候再加锁的逻辑可以知道是获取到锁的,我们看看若是没有获取锁,走的else逻辑是如何的?
java
//time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current;
if (time <= 0L) {
this.acquireFailed(threadId);
return false;
}比如说我们的time 是100秒,current 假设是1秒,则time -= 第一次获取锁耗费的时间 = 100秒 - 1秒 = 99秒,如果第一次获取锁的时间直接超过了waitTime等待最大超时时间,就会直接标记为获取锁失败,接下来的就是走else逻辑下去
java
current = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 此处为订阅锁释放事件,
// 如果当前线程通过 Redis 的 channel 订阅锁的释放事件获取得知已经被释放
// 则会发消息通知待等待的线程进行竞争
final RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> subscribeFuture = this.subscribe(threadId);
// 将订阅阻塞,阻塞时间设置为我们调用tryLock设置的最大等待时间,超过时间则返回false
if (!this.await(subscribeFuture, time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {
if (!subscribeFuture.cancel(false)) {
subscribeFuture.addListener(new FutureListener<RedissonLockEntry>() {
public void operationComplete(Future<RedissonLockEntry> future) throws Exception {
if (subscribeFuture.isSuccess()) {
RedissonLock.this.unsubscribe(subscribeFuture, threadId);
}
}
});
}
this.acquireFailed(threadId);
return false;
}简单的来说就是当前线程订阅锁释放事件,并通过 await 方法阻塞等待锁释放,一旦锁释放会发消息通知待等待的线程进行竞争
java
boolean var14;
try {
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current;
if (time > 0L) {
boolean var16;
do {
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
ttl = this.tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
if (ttl == null) {
var16 = true;
return var16;
}
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;
if (time <= 0L) {
this.acquireFailed(threadId);
var16 = false;
return var16;
}
currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (ttl >= 0L && ttl < time) {
this.getEntry(threadId).getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
this.getEntry(threadId).getLatch().tryAcquire(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;
} while(time > 0L);
this.acquireFailed(threadId);
var16 = false;
return var16;
}
this.acquireFailed(threadId);
var14 = false;
} finally {
this.unsubscribe(subscribeFuture, threadId);
}如果当前线程没有通过 Redis 的 channel 订阅锁的释放事件,获取得知已经被释放,则再次判断如果获取锁的耗时超过最大等待时间,加锁失败,上面的代码整合一下就可以变成这样
java
//如果获取锁的耗时超过最大等待时间,加锁失败
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current;
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
}接下来就是在这个最大的等待时间内进行内循环获取锁,每次time都不断的减去尝试获取锁的耗时,以及等待的耗时,然后如果说在time范围内,获取到了锁,就会返回true,如果始终无法获取到锁的话,那么就会在time指定的最大时间之后,就返回一个false
java
//在最大等待时间内循环获取锁
while (true) {
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
ttl = tryAcquire(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId);
// lock acquired
if (ttl == null) {
return true;
}
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
}
// waiting for message
currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// waiting for message,等待解锁消息
if (ttl >= 0 && ttl < time) {
subscribeFuture.getNow().getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
subscribeFuture.getNow().getLatch().tryAcquire(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
}
}三、超时锁自动释放
回到我们之前加锁的那个逻辑里去,若是我们自己定义了一个leaseTime和TimeUnit,可以看看他之前的加锁逻辑的判断
java
private <T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, final long threadId) {
if (leaseTime != -1L) {
return this.tryLockInnerAsync(leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
} else {
RFuture<Long> ttlRemainingFuture = this.tryLockInnerAsync(this.commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
ttlRemainingFuture.addListener(new FutureListener<Long>() {
public void operationComplete(Future<Long> future) throws Exception {
if (future.isSuccess()) {
Long ttlRemaining = (Long)future.getNow();
if (ttlRemaining == null) {
RedissonLock.this.scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
}
}
}
});
return ttlRemainingFuture;
}
}如果你没传递这个leaseTime的话,这个if分支是不会走的
java
<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {
this.internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
return this.commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(
this.getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command,
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " +
"redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; ",Collections.singletonList(this.getName()), new Object[]{this.internalLockLeaseTime, this.getLockName(threadId)});
}如果你自己指定了一个leaseTime,就会直接执行lua脚本去加锁,加完锁的结果就直接返回了,并不会对那个future加一个监听器以及执行定时调度任务去刷新key的生存周期,因为你已经指定了leaseTime以后,就意味着你需要的是这个key最多存在10秒钟,必须被删除
也就是说,人家在加锁的时候就设定好了,我们的锁key最多就只能存活10秒钟,而且后台没有定时调度的任务不断的去刷新锁key的生存周期
若那个锁到了10秒钟,就会自动被redis给删除,生存时间只能是10秒钟,然后就会自动释放掉了,别的客户端就可以加锁了,但是在10秒之内,其实也可以自己去手动释放锁