Appearance
一、前言回顾
java
// Acquire lock and release it automatically after 10 seconds
// if unlock method hasn't been invoked
lock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// Wait for 100 seconds and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
boolean res = lock.tryLock(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
lock.unlock();客户端A已经获取了一把锁,此时客户端B尝试去获取这把锁,默认情况下是无限制的等待,但是这里你在获取锁的时候是可以指定一个时间的,最多等待100秒的时间
如果获取不到锁直接就返回,boolean res,这个res如果是false就代表你加锁失败了,在指定时间范围内,没有获取到锁 如果获取到了锁之后,在10秒之内,没有手动释放锁,那么就自动释放锁
前篇文章入口:04_redis分布式锁(一):可重入锁源码剖析之使用场景介绍
二、redisson.getLock()解析
接下来我们就进入getLock方法里,看看它到底做了什么东西?
java
public class Redisson implements RedissonClient {
@Override
public RLock getLock(String name) {
return new RedissonLock(connectionManager.getCommandExecutor(), name);
}
//省略其他代码....
}可以关注的获取到的Lock对象是RedissonLock对象,里面封装了一个ConnectionManager里获取的一个CommandExecutor,CommandExecutor是什么东西?
从名字看里面一定是封装了一个跟redis之间进行通信的一个Cconnection连接对象
java
public interface ConnectionManager {
//省略其他关键代码.....
CommandSyncService getCommandExecutor();
}
public class MasterSlaveConnectionManager implements ConnectionManager {
private final CommandSyncService commandExecutor;
public CommandSyncService getCommandExecutor() {
return this.commandExecutor;
}
//省略其他关键代码.....
}java
public class CommandSyncService extends CommandAsyncService implements CommandExecutor {
public <T, R> R read(String key, RedisCommand<T> command, Object... params) {
return this.read(key, this.connectionManager.getCodec(), command, params);
}
public <T, R> R read(String key, Codec codec, RedisCommand<T> command, Object... params) {
RFuture<R> res = this.readAsync(key, codec, command, params);
return this.get(res);
}
//省略其他关键代码.....
}
public class CommandAsyncService implements CommandAsyncExecutor {
//省略其他关键代码.....
public <T, R> RFuture<R> readAsync(String key, Codec codec, RedisCommand<T> command, Object... params) {
RPromise<R> mainPromise = this.createPromise();
NodeSource source = this.getNodeSource(key);
this.async(true, source, codec, command, params, mainPromise, 0, false, (RFuture)null);
return mainPromise;
}
public <V> V get(RFuture<V> future) {
if (!future.isDone()) {
final CountDownLatch l = new CountDownLatch(1);
future.addListener(new FutureListener<V>() {
public void operationComplete(Future<V> future) throws Exception {
l.countDown();
}
});
boolean interrupted = false;
while(!future.isDone()) {
try {
l.await();
} catch (InterruptedException var5) {
interrupted = true;
break;
}
}
if (interrupted) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
if (future.isSuccess()) {
return future.getNow();
} else {
throw this.convertException(future);
}
}
}那么我们就可以知道CommandExecutor命令执行器,封装了一个redis连接的命令执行器,可以执行一些set、get redis的一些操作,用来执行底层的redis命令的就可以了
接下来回到刚刚new RedissonLock(this.connectionManager.getCommandExecutor(), name);
java
public class RedissonLock extends RedissonExpirable implements RLock {
//省略其他关键性代码...
public RedissonLock(CommandAsyncExecutor commandExecutor, String name) {
super(commandExecutor, name);
this.commandExecutor = commandExecutor;
this.id = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getId();
this.internalLockLeaseTime = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout();
this.entryName = id + ":" + name;
}
}在这个RedissonLock的构造函数里面,建议关注的代码internalLockLeaseTime这东西,它是和跟watchdog看门狗有关系的
三、RedissonLock.getLock()解析
对于interlnalLockLeaseTime,我们可以根据构造函数里的commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(),去看看他是怎么赋值的
java
public interface ConnectionManager {
//省略其他关键代码.....
CommandSyncService getCommandExecutor();
Config getCfg();
}
public class MasterSlaveConnectionManager implements ConnectionManager {
private final CommandSyncService commandExecutor;
private final Config cfg;
public CommandSyncService getCommandExecutor() {
return this.commandExecutor;
}
//省略其他关键代码.....
}
public class Config {
public Config() {
this.transportMode = TransportMode.NIO;
this.lockWatchdogTimeout = 30000L;
this.keepPubSubOrder = true;
this.addressResolverGroupFactory = new DnsAddressResolverGroupFactory();
}
//省略其他关键代码.....
}接下来我们从redisson执行getLock获取到锁,现在可以看看RedissonLock它是怎么执行lock这个步骤的
java
public class RedissonLock extends RedissonExpirable implements RLock {
//省略其他关键性代码...
public RedissonLock(CommandAsyncExecutor commandExecutor, String name) {
super(commandExecutor, name);
this.commandExecutor = commandExecutor;
this.id = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getId();
this.internalLockLeaseTime = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout();
this.entryName = id + ":" + name;
}
@Override
public void lock() {
try {
this.lockInterruptibly();
} catch (InterruptedException var2) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
@Override
public void unlock() {
try {
get(unlockAsync(Thread.currentThread().getId()));
} catch (RedisException e) {
if (e.getCause() instanceof IllegalMonitorStateException) {
throw (IllegalMonitorStateException)e.getCause();
} else {
throw e;
}
}
public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
this.lockInterruptibly(-1L, (TimeUnit)null);
}
public void lockInterruptibly(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
Long ttl = this.tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
if (ttl != null) {
RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> future = this.subscribe(threadId);
this.commandExecutor.syncSubscription(future);
try {
while(true) {
ttl = this.tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
if (ttl == null) {
return;
}
if (ttl >= 0L) {
this.getEntry(threadId).getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
this.getEntry(threadId).getLatch().acquire();
}
}
} finally {
this.unsubscribe(future, threadId);
}
}
}
}发现我们如果没有传递leaseTime和unit,默认走的是-1和null,紧接着就是走到tryAcquire这个方法,往里继续看详情处理了什么内容
java
private Long tryAcquire(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
return (Long)this.get(this.tryAcquireAsync(leaseTime, unit, threadId));
}
private <T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, final long threadId) {
if (leaseTime != -1L) {
return this.tryLockInnerAsync(leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
} else {
RFuture<Long> ttlRemainingFuture = this.tryLockInnerAsync(
this.commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(),
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
ttlRemainingFuture.addListener(new FutureListener<Long>() {
public void operationComplete(Future<Long> future) throws Exception {
if (future.isSuccess()) {
Long ttlRemaining = (Long)future.getNow();
if (ttlRemaining == null) {
RedissonLock.this.scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
}
}
}
});
return ttlRemainingFuture;
}
}
<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {
this.internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
return this.commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(
this.getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command,
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); return nil; end; if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); return nil; end; return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);",
Collections.singletonList(this.getName()), new Object[]{this.internalLockLeaseTime, this.getLockName(threadId)});
}至此我们就找到有个lua脚本,针对redis加锁的这么一个底层的命令
java
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " +
"redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
"return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);"第一行if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then,KEYS[1] 一看就是我们设置的那个锁的名字,先执行了redis的exists的指令,判断一下,如果“anyLock”这个key不存在,那么就进行加锁,加锁的指令:
java
"redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +hset,它是redis的一个指令,相当于是在redis的一个map数据结构里设置一个key value,相当于有一个anyLock的map结构,同时在map里面放着一对kv。而pexpire KEYS[1] ARGV[1],其实就是设置一个key的过期时间,紧接着我们可以发现后面还有一段lua脚本
java
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +hexits KEYS[1] ARGV[2],这个意思就是说针对KEYS[1](anyLock)这个名字的一个map,里面是否存在一个ARGV[2]的一个key,如果是存在的话,hincrby KEYS[1] ARGV[2] 1,将anyLock这个map中的这个key的值累加1,同时又执行了一下pexpire ,再一次将anyLock这个key的有效期又设置一次
接下来我们看return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);这行指令,其实是pttl这个指令,就是返回anyLock这个key当前还剩下的一个有效的存活期,就是当前这个key还能存活多少毫秒,或者多少秒这样子
至此我们上面加锁的逻辑就是这样,接着往下走this.commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync�
java
public class CommandAsyncService implements CommandAsyncExecutor {
public <T, R> RFuture<R> evalWriteAsync(String key, Codec codec, RedisCommand<T> evalCommandType, String script, List<Object> keys, Object... params) {
NodeSource source = this.getNodeSource(key);
return this.evalAsync(source, false, codec, evalCommandType, script, keys, params);
}
//省略其他关键性代码....
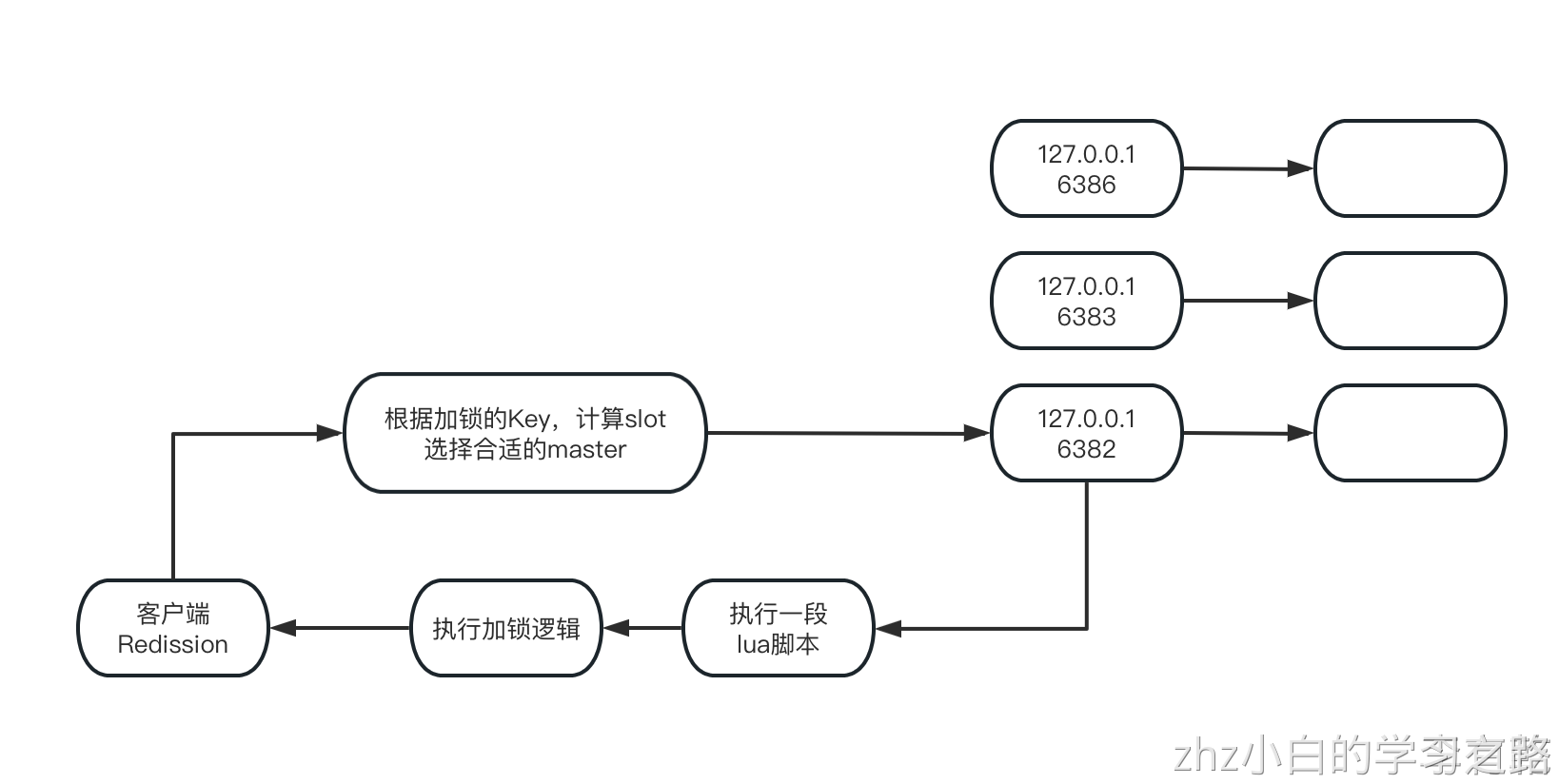
}看着方法的名称,可以推测是根据anyLock这个key,尝试去获取到一个NodeSource的这么一个东西,我们可以认为说,我们现在不是有3主3从的一个redis集群,是不是有可能说他是通过key获取其中一个NodeSource?
这个NodeSource有可能就是3个master实例中的一个,有可能就是说对这个key的设置,就释放在3个master的其中一个上而已
java
private NodeSource getNodeSource(String key) {
int slot = this.connectionManager.calcSlot(key);
MasterSlaveEntry entry = this.connectionManager.getEntry(slot);
return new NodeSource(entry);
}在redis cluster,默认的slot数量是16384,无论你创建的是多大的一个redis cluster,他统一有一个slot的一个划分,就是将集群的存储空间划分为16384个slot,这16384个slot就平均分布在各个master实例上
3个master,每个master实例有5000多slot。这里就可以猜出意思:那么在针对redis cluster读写操作的时候,先会去基于hash算法计算这个slot,anyLock这个key,13434,算出来是这个slot,相当于是针对“anyLock”这个key计算出来一个hash值,然后将这个hash值对16384这个slot数量进行取模,int slot = connectionManager.calcSlot(key);
java
public int calcSlot(String key) {
if (key == null) {
return 0;
} else {
int start = key.indexOf(123);
int result;
if (start != -1) {
result = key.indexOf(125);
key = key.substring(start + 1, result);
}
result = CRC16.crc16(key.getBytes()) % 16384;
this.log.debug("slot {} for {}", result, key);
return result;
}
}取模之后就可以拿到当前这个“anyLock”的key对应的是哪个slot,而MasterSlaveEntry entry = connectionManager.getEntry(slot);,这行代码是什么意思?就是算出来了一个slot,就是根据这个slot的编号,获取到这个slot是属于哪个master实例的
将这entry打印出来可以看到是
java
MasterSlaveEntry [
masterEntry=[
freeSubscribeConnectionsAmount=1,
freeSubscribeConnectionsCounter=50,
freeConnectionsAmount=32,
freeConnectionsCounter=64,
freezed=false,
freezeReason=null,
client=[addr=redis://localhost:6382],
nodeType=MASTER,
firstFail=0
]
]此时就是已经知道了,其实必须是将加锁的那段lua脚本,放到redis://127.0.0.1:6382这个master实例上去执行,完成加锁的操作,接着往下走,看看他的参数是什么?
java
public <T, R> RFuture<R> evalWriteAsync(String key, Codec codec, RedisCommand<T> evalCommandType, String script, List<Object> keys, Object... params) {
NodeSource source = this.getNodeSource(key);
return this.evalAsync(source, false, codec, evalCommandType, script, keys, params);
}
private <T, R> RFuture<R> evalAsync(NodeSource nodeSource, boolean readOnlyMode, Codec codec, RedisCommand<T> evalCommandType, String script, List<Object> keys, Object... params) {
RPromise<R> mainPromise = this.createPromise();
List<Object> args = new ArrayList(2 + keys.size() + params.length);
args.add(script);
args.add(keys.size());
args.addAll(keys);
args.addAll(Arrays.asList(params));
this.async(readOnlyMode, nodeSource, codec, evalCommandType, args.toArray(), mainPromise, 0, false, (RFuture)null);
return mainPromise;
}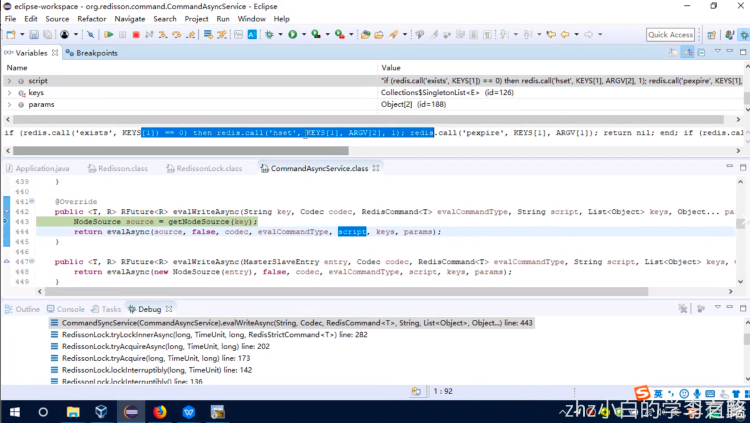 keys,是一个数组,[anyLock],这个其实对应的就是上面分析的那个脚本里的KEYS[1] params,是一个参数,[30000,8743c9c0-0795-4907-87fd-6c719a6b4586:1],代表的其实就是ARGV[1]和ARGV[2]
keys,是一个数组,[anyLock],这个其实对应的就是上面分析的那个脚本里的KEYS[1] params,是一个参数,[30000,8743c9c0-0795-4907-87fd-6c719a6b4586:1],代表的其实就是ARGV[1]和ARGV[2]
把参数和数组带入回到我们这串lua脚本里去
java
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " +
"redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
"return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);"
//KEYS[1] = anyLock
//ARGV[1] = 30000
//ARGV[2] = 8743c9c0-0795-4907-87fd-6c719a6b4586:18743c9c0-0795-4907-87fd-6c719a6b4586,代表的是一个UUID,其实就是这个客户端上的一个ConnectionManager的这么一个id,1是什么呢?其实就是threadId,大体上可以认为是一个客户端的一个线程对应的唯一的标识
ARGV[2],代表的就是一个客户端上的一个线程,对这个key进行了加锁
java
//对于下面的hexists部分就是
//anyLock这个key是否存在?
//hset anyLock 8743c9c0-0795-4907-87fd-6c719a6b4586:1 1
//anyLock就对应一个map数据结构(hash)
{
“8743c9c0-0795-4907-87fd-6c719a6b4586:1”: 1
}pexpire anyLock 30000:anyLock这个key只能存活30000毫秒,30秒,默认情况下,你使用redisson加锁,其实不是无限制的不停的可以拥有这把锁的,默认情况下给你设置的一个锁的有效期就是30秒